In recent years, the concept of accessibility in gaming has gained significant traction, evolving from a niche concern to a critical aspect of game design. Accessibility in gaming refers to the practice of designing and developing games that are playable by as many people as possible, including those with physical, sensory, cognitive, or other disabilities. This approach ensures that games are inclusive, allowing everyone to participate in the rich experiences that gaming offers. As the gaming community continues to grow and diversify, the importance of accessibility has become increasingly apparent, with more developers and studios recognizing the need to create games that cater to a wider range of players.
The recognition of accessibility in gaming is not a recent development; discussions around this issue have been ongoing for years. Within the later 2010s, the conversation around making games more accessible began to gain momentum, driven by advocates and developers who understood the importance of inclusivity. However, the roots of this movement extend even further back, with pioneers like Ian Hamilton advocating for accessibility in gaming since the mid-2000s. Their early efforts laid the groundwork for the accessibility standards we see today, as the industry slowly but surely began to embrace the idea that games should be designed with all players in mind, regardless of their abilities.
A Historical Perspective

The history of accessibility in gaming is marked by a series of key milestones and the tireless efforts of early advocates who recognized the need for inclusivity long before it became a mainstream concern. One of the earliest and most influential figures in this movement is Ian Hamilton, whose work has been instrumental in shaping accessibility standards in gaming. Beginning in 2006, Hamilton's efforts at the BBC were pioneering, as he helped create some of the first switch-accessible games for children. These early initiatives were crucial in demonstrating that accessible game design was not only possible but also highly impactful.
Hamilton's influence extended beyond the BBC, as he turned his attention to the broader gaming industry in 2011. His advocacy and consulting work have been vital in raising awareness and setting the bar for accessibility across the industry. Through his involvement in creating the first accessible gaming guidelines at the BBC and later coordinating gameaccessibilityguidelines.com, Hamilton laid the foundation for many of the standards that developers now follow. His work has inspired a new generation of designers and studios to consider accessibility from the earliest stages of game development, making it an integral part of the creative process rather than an afterthought.
Early accessibility advocates like Hamilton were joined by other pioneers who pushed the boundaries of what was possible in game design. These efforts led to the development of the first games designed specifically with accessibility in mind, setting a precedent for the industry. For instance, games like The Last of Us Part II have become benchmarks in accessibility, offering a wide range of features that cater to players with various disabilities. These early successes were crucial in demonstrating the importance of accessible game design and have paved the way for the more comprehensive and inclusive gaming experiences we see today.
Current State of Accessibility in Gaming
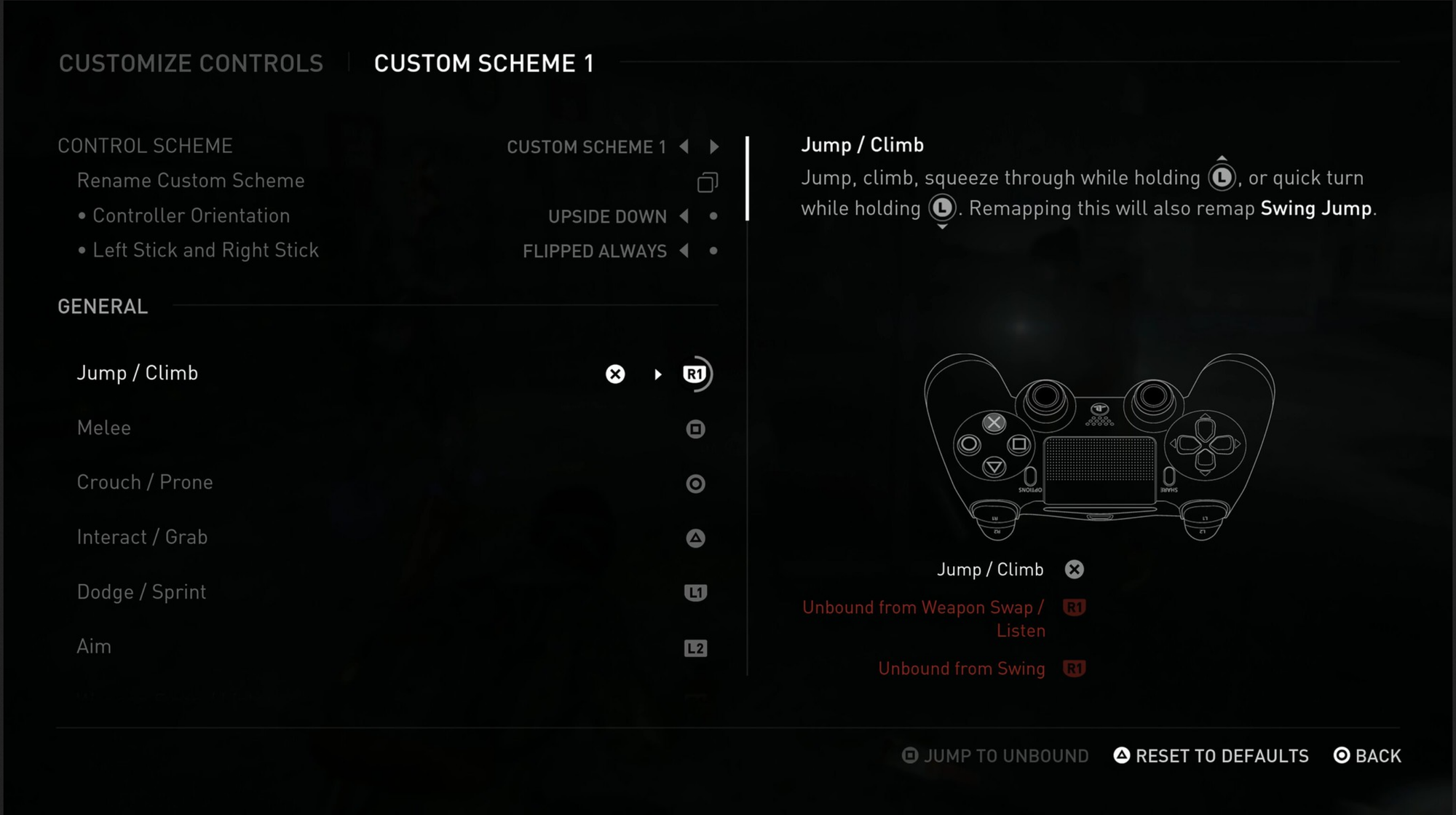
Today, accessibility in gaming has moved from being a niche consideration to a fundamental aspect of game design, with developers increasingly recognizing the importance of creating inclusive experiences. Many studios now incorporate accessibility features from the outset, ensuring that games can be enjoyed by a broader audience, including players with disabilities. This shift is evident in the growing number of games that offer a wide range of accessibility options, allowing players to tailor their gaming experience to their individual needs.
One of the most prominent examples of successful accessibility implementation is The Last of Us Part II. This game is often lauded as a benchmark in the industry, offering over 60 accessibility options that cater to players with various disabilities. These features include customizable controls, text-to-speech, high contrast modes, and options for reducing motion sickness. The game’s commitment to accessibility has set a new standard, demonstrating how thoughtful design can make games more inclusive without compromising on gameplay or narrative depth.
However, while there are shining examples of accessibility done right, the industry still has areas where it falls short. Some games, particularly those from smaller studios or those with limited resources, may struggle to implement comprehensive accessibility features. Additionally, there are still instances where games fail to consider the diverse needs of their audience, resulting in experiences that are inaccessible to certain players. This highlights the ongoing need for awareness, education, and resources to support developers in creating accessible games.
In addition to physical and sensory disabilities, the gaming industry is beginning to acknowledge the importance of including neurodivergent users in the design process. Neurodivergent players, who may have conditions such as autism, ADHD, or dyslexia, often face unique challenges in gaming. Some developers are now starting to consider these needs by offering features such as simplified controls, clear and consistent UI design, and the ability to adjust sensory inputs like sound and lighting. While progress in this area is still in its early stages, the growing awareness of neurodivergent players’ needs is a positive step towards more inclusive game design. The inclusion of neurodivergent perspectives in playtesting and design discussions could further enhance these efforts, ensuring that games are truly accessible to all.
Impact on Players with Disabilities

The impact of accessible game design on players with disabilities is profound, offering not just entertainment but also a sense of inclusion and empowerment. For many players, accessible features can mean the difference between being able to fully engage with a game or being excluded from an experience that others might take for granted. Personal stories from players with disabilities highlight the importance of these features and the joy that comes from being able to participate in the gaming community.
Steve Saylor, a blind gamer and prominent accessibility advocate, has often shared how accessibility options have transformed his gaming experiences. Accessibility isn’t just about adding features to a game—it’s about making sure everyone has the chance to experience the joy and connection that gaming provides. Saylor’s involvement as an accessibility consultant on major titles like The Last of Us Part II and Forza Motorsport has helped ensure that these games are not only playable but truly enjoyable for players with disabilities.
Another powerful example comes from Manny Wooden, a quadriplegic gamer who once believed he would never be able to play games again after his injury. Thanks to remapping options and other accessibility features, Manny was able to return to gaming, describing it as a lifeline that provided him with a sense of normalcy and independence during a challenging time in his life. "When my injury happened, I got extremely depressed. Because I had no finger movement, I figured there was nothing I could really do anymore. Eventually, I found help to mod a controller. Thanks to remapping options, I’ve been gaming ever since," he shared.
These stories underscore the real-world impact of accessibility in gaming, showing how thoughtful design can open new worlds for players with disabilities. For many, gaming is not just a pastime but a crucial way to connect with others, experience new narratives, and engage in interactive storytelling. The growing focus on accessibility is making these experiences possible for a wider range of players, demonstrating the importance of continuing to push for more inclusive game design.
Challenges and Future Directions

Despite the significant progress made in recent years, developers still face several challenges when it comes to implementing accessibility features in games. One of the primary obstacles is resource constraints. Developing comprehensive accessibility options requires time, money, and expertise, which can be particularly challenging for smaller studios with limited budgets. Additionally, retrofitting accessibility features into a game late in the development process can be costly and complicated, underscoring the need for accessibility to be considered from the very beginning of the design phase.
Another challenge is the lack of awareness and education about accessibility among developers. While there is growing recognition of the importance of accessible game design, many developers may not fully understand the needs of players with disabilities or how to address them effectively. This can lead to unintentional oversights or the inclusion of features that are inaccessible to certain players. As Ian Hamilton’s guidelines emphasize, incorporating disabled players into the development process through playtesting and consultation is crucial. This not only helps developers identify potential barriers but also fosters a culture of inclusivity within the industry.
Looking ahead, the future of accessibility in gaming holds great promise, driven by both technological advancements and a growing commitment to inclusivity. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and adaptive controllers have the potential to revolutionize accessibility in games. For instance, AI could be used to create dynamic difficulty adjustments that respond to a player’s abilities in real time, making games more accessible to a wider range of users. Similarly, advancements in voice recognition, haptic feedback, and eye-tracking technology could provide new ways for players with disabilities to interact with games.
Moreover, as awareness continues to grow, we can expect to see accessibility considerations increasingly integrated into the game development process from the ground up. This shift is already happening in some studios, where accessibility is becoming a core component of design rather than an afterthought. As more developers recognize the value of inclusive game design, the industry as a whole is likely to move towards a future where accessibility is a standard part of game development, benefiting both players and creators alike.
The ongoing challenge will be to ensure that these advancements are widely adopted across the industry, from indie developers to AAA studios, and that accessibility remains a priority even as new technologies and gaming trends emerge. With continued advocacy, education, and the inclusion of diverse voices in the development process, the future of accessibility in gaming looks bright, offering the promise of truly inclusive gaming experiences for all players.
The Path Forward: Ensuring a More Inclusive Future in Gaming
Accessibility in gaming is not just a technical consideration; it is a fundamental aspect of creating inclusive experiences that allow everyone to enjoy the richness of interactive entertainment. The positive impact of accessible game design cannot be overstated, as it opens up the world of gaming to individuals who might otherwise be excluded due to physical, sensory, or cognitive barriers. By implementing thoughtful accessibility features, developers and studios can ensure that their games are not only more enjoyable for players with disabilities but also richer and more rewarding for all players.
While significant progress has been made in recent years, with notable successes in both indie and AAA games, there is still much work to be done. The challenges of resource constraints, lack of awareness, and the need for more inclusive design practices continue to be hurdles that the industry must overcome. However, the growing commitment to accessibility, coupled with technological advancements, offers hope that these challenges can be met head-on.
The journey towards fully inclusive gaming is ongoing, and it requires the collective effort of developers, studios, and players alike. Developers must continue to prioritize accessibility from the earliest stages of design, incorporating feedback from disabled players and staying informed about best practices. Studios should allocate the necessary resources and foster a culture that values inclusivity. And players, too, have a role to play by advocating for and supporting accessible games, helping to drive demand for more inclusive experiences.
In conclusion, accessibility in gaming is not just a matter of good design—it is a moral imperative that ensures everyone has the opportunity to participate in the joys of gaming. By continuing to push for greater accessibility, we can create a gaming landscape where no one is left behind, and where every player, regardless of ability, can find their place in the world of games.